<< 5.1 Convergence in Probability.md | 5.3 Central Limit Theorem.md >>
Definition 5.2.1: Converges in distribution
Let
- : Sequence of random variables, with
- : cdf of
- : Random variable
- : cdf of
- denote the set of all points where is continuous
If
Then
Link to original
- We say converges in distribution to
- We write
Remark 5.2.2: Stirling’s formula
In advanced calculus, the following approximation is derived:
Theorem 5.2.1
Theorem 5.2.2
Note
Although in
it is said stated that , the converse is actually true. So we use instead.Link to original
- Hogg, R. V., McKean, J. W., & Craig, A. T. (2019). Introduction to Mathematical Statistics (8th ed.). Pearson.
Theorem 5.2.3
Suppose
Then
Theorem 5.2.4
Suppose
- is continuous
Then
Theorem 5.2.5: Slutsky’s theorem
Let
- : Random variables
- : Constants
If
Then
Definition 5.2.2: Bounded in probability
Let
- : Sequence of Random variables
If
Then we say is bounded in probability
Link to original
Theorem 5.2.6
Let
- : Sequence of random variables
- : Random variable
If
Then is bounded in probability
Theorem 5.2.7
Let : Sequences of random variables
Suppose
- bounded in probability
Then
TODO: Make sense of 5.2.8, 5.2.9
Theorem 5.2.8
Let : Sequence of random variables
Suppose
- bounded in probability
Then
Theorem 5.2.9
Let : Sequence of random variables
Suppose
- is differentiable at
Then
Theorem 5.2.10: MGF technique
Let
- : Sequence of random variables, with
- mgf which exists for for all
- : Random variable, with
- mgf which exists for
If
Then
Note
The MGF uniquely determines a distribution (when it exists in a neighborhood of zero). So if the MGFs converge, the underlying distributions must also converge.
Theorem 0
Let
- : Sequence of random variables
- : Constant
Then
Note
For convergence to a constant , convergence in probability and convergence in distribution are equivalent.
Theorem 1
Let
- : Random variable
- : cdf of
Then
Theorem 2
Let
- : Random variable
- : cdf of
If
Then
Theorem 2.5
Let
- : Sequences of random variables
- : Constants
If
Then
Theorem 3
Let
- : Random variable
- : Random variable
If
Then
Proposition 5.2.16
If
Then
Exercise
Exercise 5.1 of Hogg & Craig 5th ed.
Let denote the mean of a random sample of size from a distribution that is . Find the limiting distribution of .
Based on Theorem 5.1.1: Weak law of large numbers,
Consequently, the limiting distribution of is .
Hogg & Craig 5th ed. 5.7.
Let
- : Sequence of random variable, with
Prove that converges in probability to
Answer
Karena , berarti dan . Misalkan . Maka,
Misalkan . Berdasarkan teorema Chebyshev,
Sehingga diperoleh
Berdasarkan definisi konvergen dalam probabilitas, terbukti bahwa
Hogg & Craig 5th ed. 5.10.
Let
- : -th Order statistic from random sample of size , with
Prove that converges in probability to
Answer
Dari Example 1 Section 5.1
converges in distribution to a random variable that has a degenerate distribution at the point .
Artinya, . Berdasarkan teorema 5.2.2, diperoleh . Misalkan . Berdasarkan teorema 5.1.4, diperoleh , sehingga terbukti bahwa konvergen dalam probabilitas ke
Hogg & Craig 5th ed. 5.12.
Let
- : Sequence of random variables, with
Find the limiting distribution of
Answer
Diketahui mgf dari distribusi Chi-square adalah , untuk . Karena , mgf dari dapat diperoleh dengan
Karena , dengan memisalkan , , dan , dapat diperoleh
Misalkan variabel acak dengan mgf . Andaikan berdistribusi degenerate ke , yang berakibat . Karena , berdasarkan teorema 5.2.10, diperoleh . Terbukti bahwa limiting distribution dari adalah .
Hogg & Craig 5th ed. 5.13.
Let
- : Random variable, with
Approximate
Answer
Hogg & Craig 5th ed. 5.15.
Let
- : Sequence of random variable, with
Show that the limiting distribution of is normal with mean zero and variance .
Answer
Diketahui mgf dari distribusi adalah . Dapat diperoleh mgf dari :
Menggunakan Maclaurun series pada , perluaskan menjadi
Sehingga diperoleh
Misalkan variabel acak dengan berdistribusi . Artinya, . Berdasarkan teorema 5.2.10, karena , maka , sehingga . Terbukti bahwa limiting distribution dari adalah distribusi normal dengan mean dan variansi .
Example 1

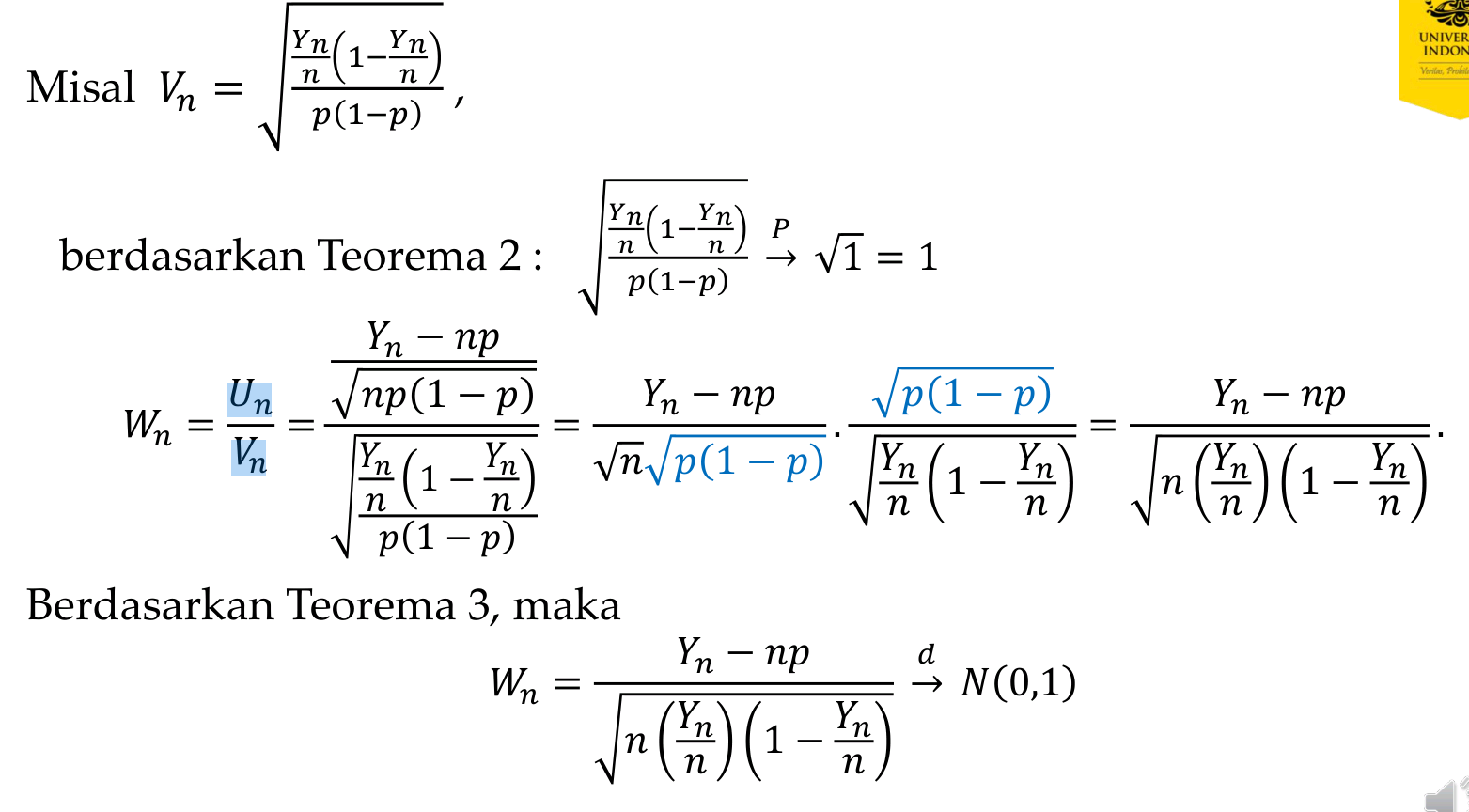
Example 2

Footnotes
-
Taken from Theorem 1 in Section 5.2: Convergence in Probability of Hogg & Craig 5th ed. ↩