Definition
Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of vertices and edges. The vertices are sometimes also referred to as nodes and the edges are lines or arcs that connect any two nodes in the graph. More formally a Graph is composed of a set of vertices( ) and a set of edges( ).
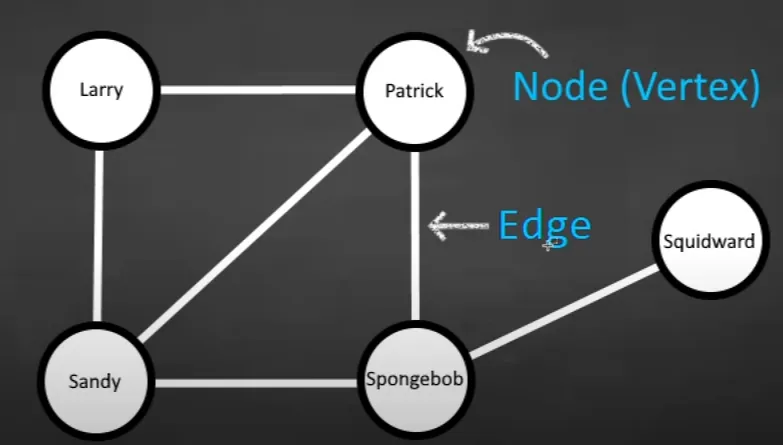
Terms
- Vertex/node: The data/values in the graph.
- Edge: Connection or relationship between two vertexes.
- Undirected graph: Graph where the edges does not have a direction, i.e., each edge can be traversed in both direction.
- Directed graph: Graph where the edges have a direction. e.g., vertex have an edge going to vertex , but not the otherway around.
- Two vertexes are said to be adjacent, if there is an edge connecting the vertexes.
Graph as adjacency matrix
Graph can be represented using an adjacency matrix, by forming a matrix, and assigning each entry as the edge of th and th vertex.
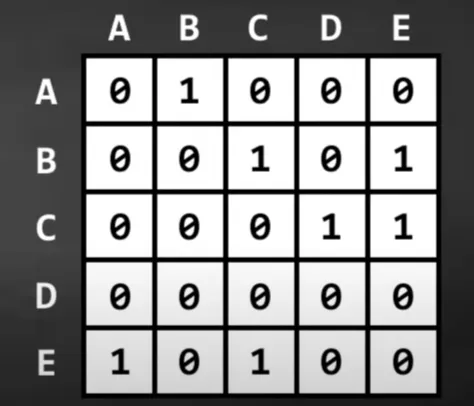
Properties
- Access time complexity:
- Space complexity:
Graph as adjacency list
Represent graph with a collection of linked lists, where the first element in each list correspond to a vertex in the graph, and the following elements correspond to the neighboring vertex.
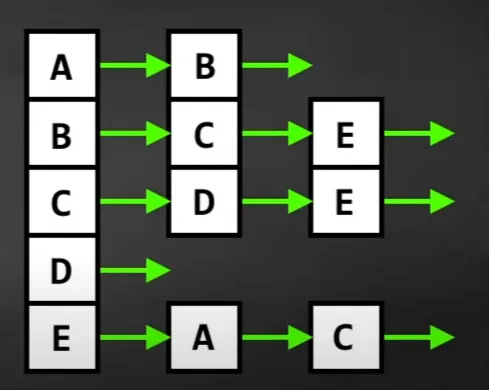
Properties
- Access time complexity:
- Space complexity:
Implementation
Algorithms
List
Stack
Singly Linked Lists
- Reverse Linked List
- Merge Two Sorted Linked Lists
- Singly Linked List Operations
- Merge K Sorted Linked Lists
Doubly Linked List
Queue
Sorting algorithm
Bucket sort