- Pick the starting node and visit it.
- Visit all the unvisited neighbors of the current node (in order).
- Move to the next node in the queue.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 until there are no more nodes in the queue.
Visualization
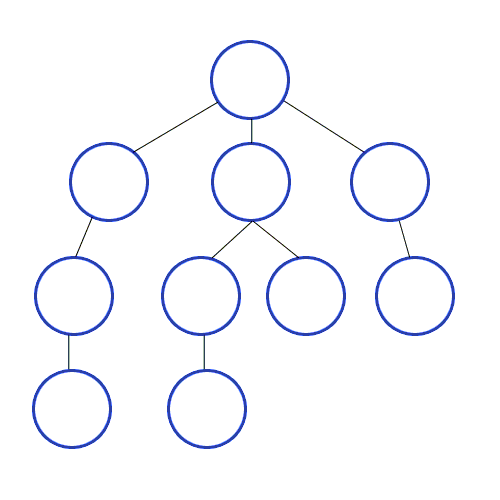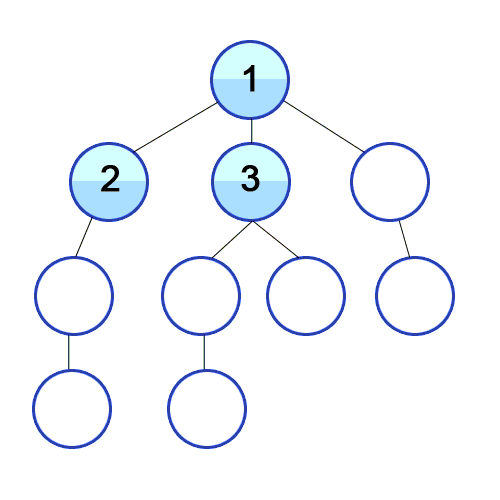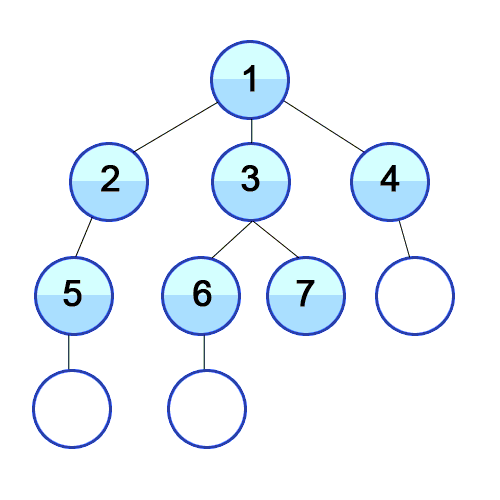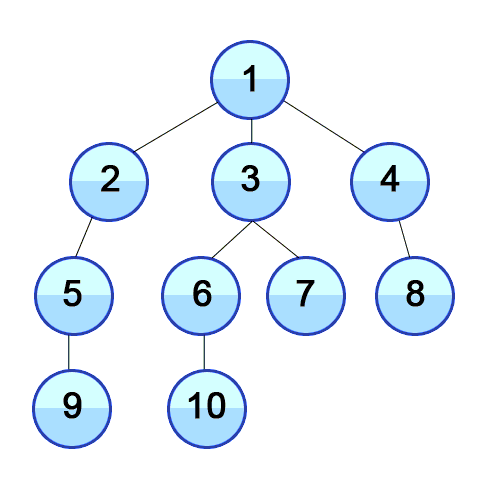
BFS in tree
BFS in maze
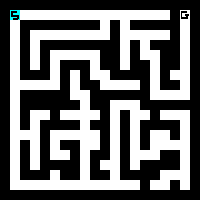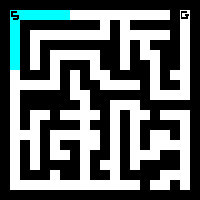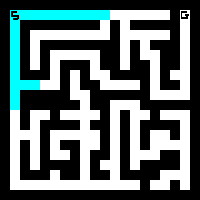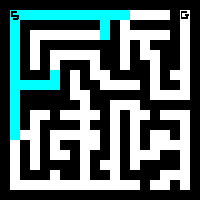
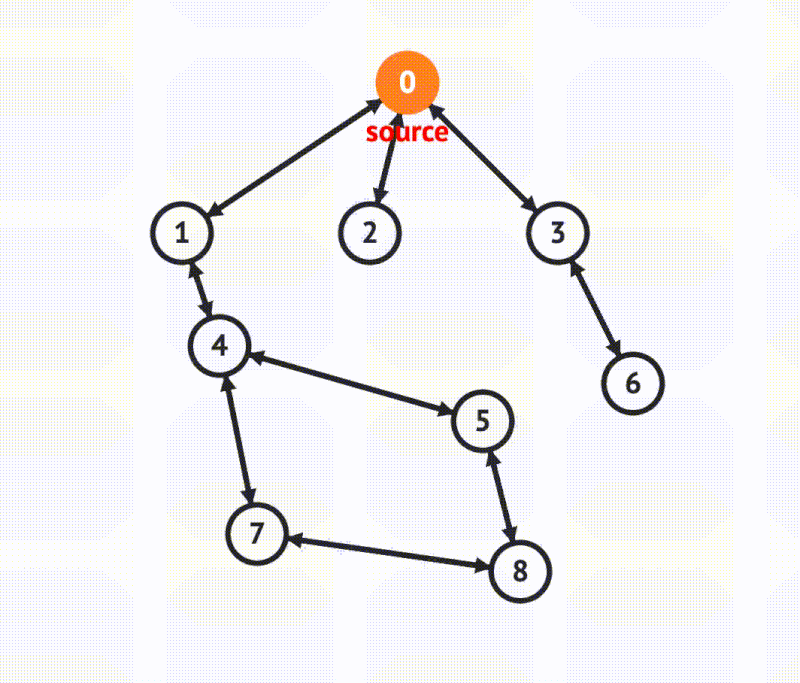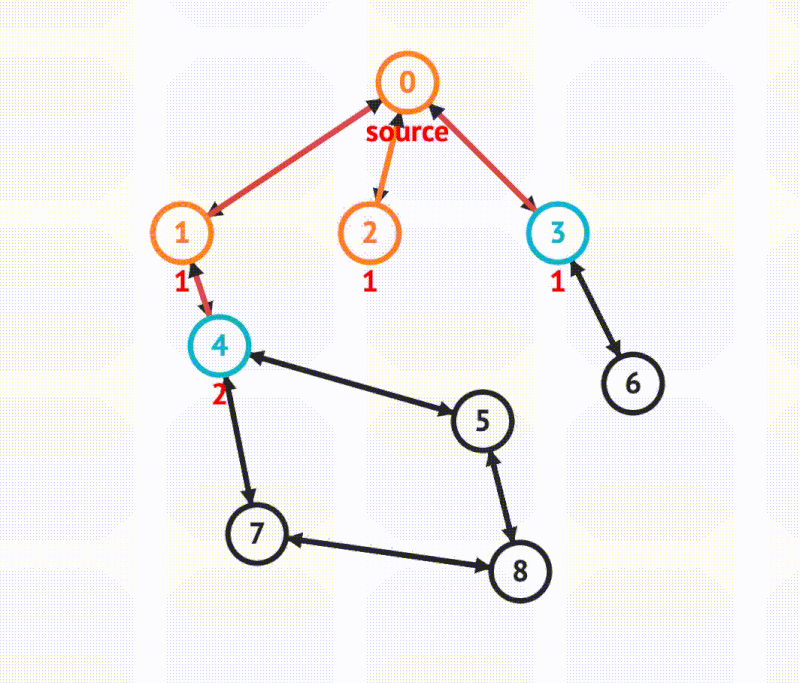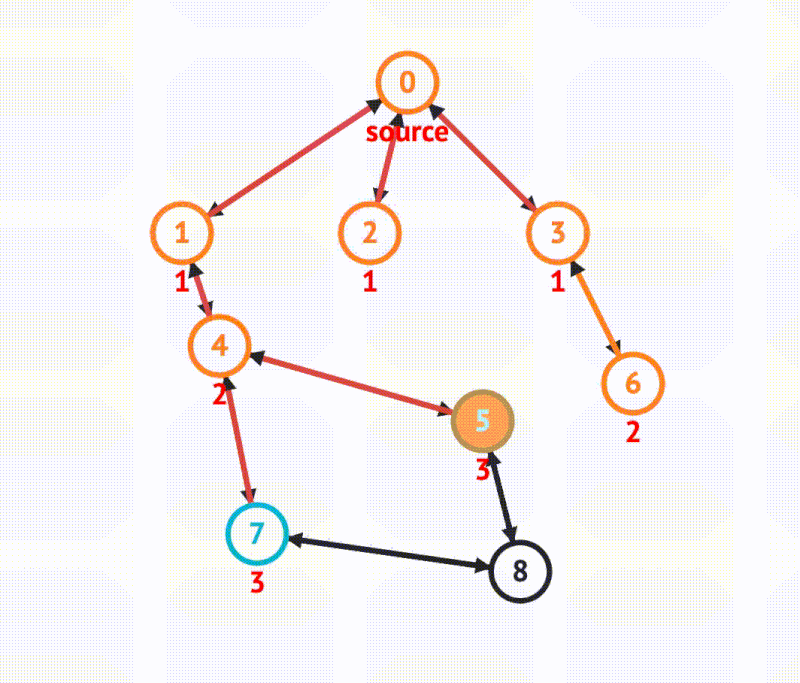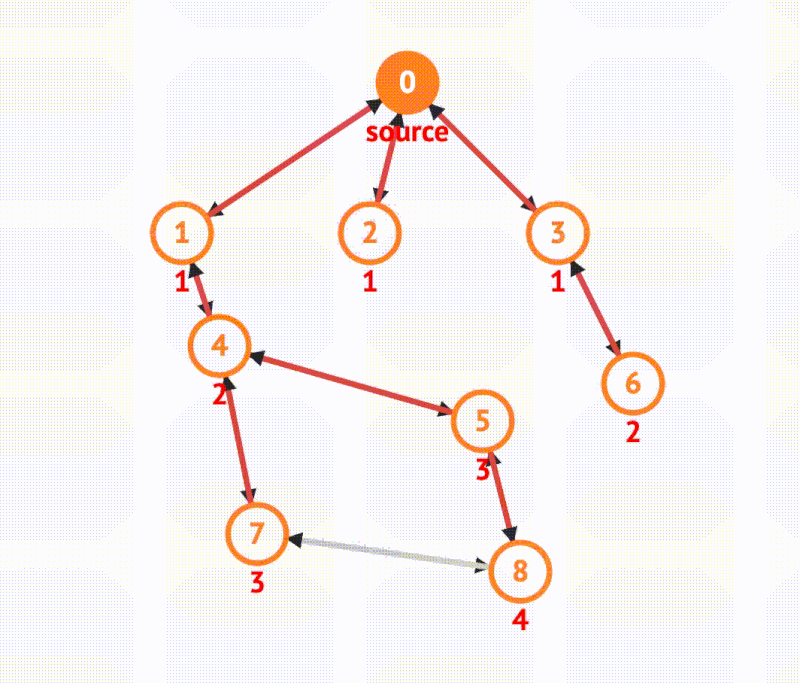
BFS in graph
DFS vs BFS
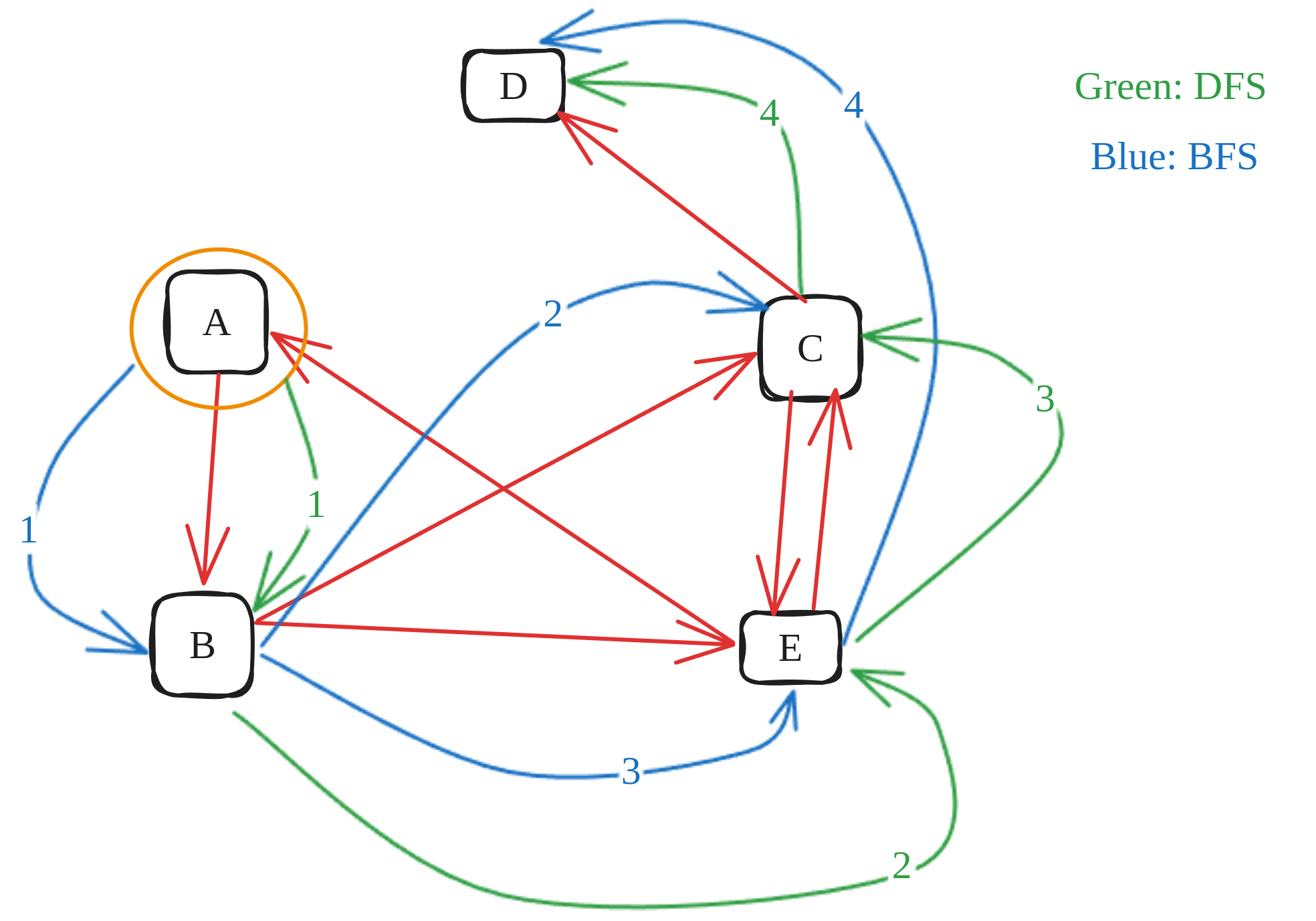
Algorithm
There is one primary approach to implement a breadth first search for graphs, that is, using a queue.
- Prepare variables
to_visit: Stack to store verteces that needs to be visited. Initial value is the start vertex.visited: Hash set to store verteces that has already been visited.path: List to store all verteces traversed byto_visit.
- Keep dequeueing
to_visitqueue while it’s not empty. For each vertex. - If the current vertex is already in
visited, we skip it. - If not, we add the vertex to
visitedandpath. - For each adjacent vertex of the current vertex:
- Add the adjacent vertex into the queue.
Implementation
To see the complete code, go to Graph
def bfs(self, start: _Vertex) -> list[_Vertex]:
to_visit: Deque[_Vertex] = deque([start])
visited: set[_Vertex] = set()
path: list[_Vertex] = []
while len(to_visit) != 0:
curr = to_visit.popleft()
if curr not in visited:
visited.add(curr)
path.append(curr)
for neigh in self._get_neighs(curr):
to_visit.append(neigh)
return path
@abstractmethod
def _get_neighs(self, vertex: _Vertex) -> list[_Vertex]: ...