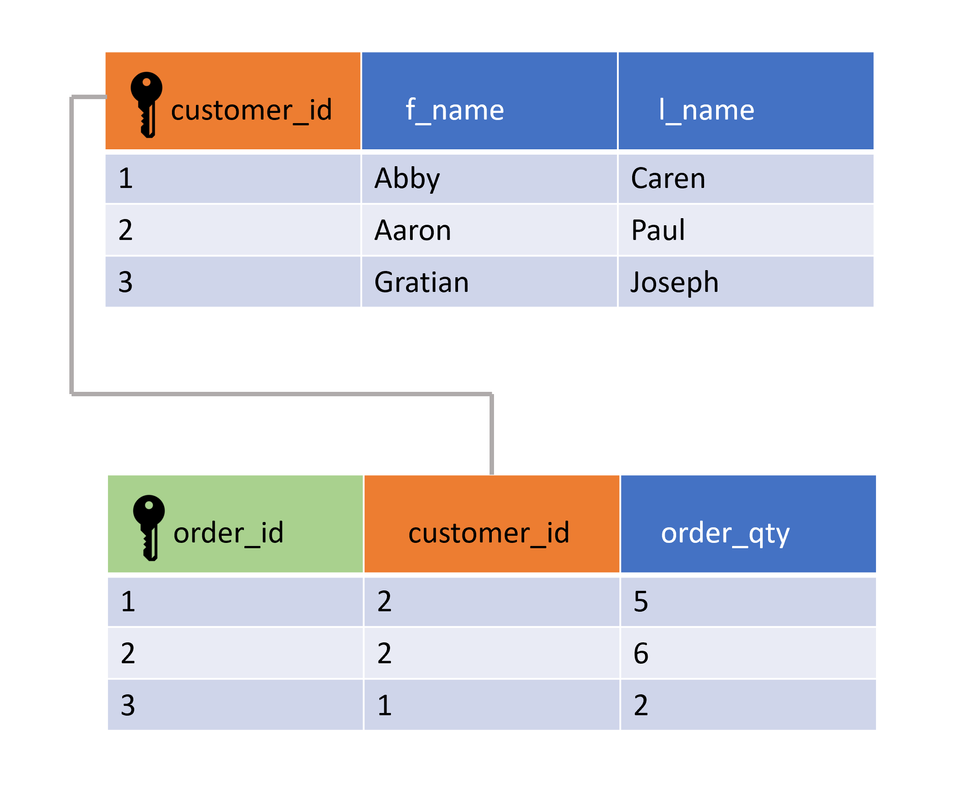
Primary key
A primary key column in a SQL table is used to uniquely identify each record in that table. A primary key cannot be NULL. In the example, customer_id is the primary key. The same value cannot re-occur in a primary key column. Primary keys are often used in JOIN operations.
Foreign key
A foreign key is a reference in one table’s records to the primary key of another table. To maintain multiple records for a specific row, the use of foreign key plays a vital role. For instance, to track all the orders of a specific customer, the table order (illustrated at the bottom of the image) can contain a foreign key.
WITH clause
Stores result set of a query in a temporary table.
WITH temporary_movies AS (
SELECT *
FROM movies
)
SELECT *
FROM temporary_movies
WHERE year BETWEEN 2000 AND 2020;UNION clause
Combine multiple result sets.
SELECT name
FROM first_names
UNION
SELECT name
FROM last_namesJoins
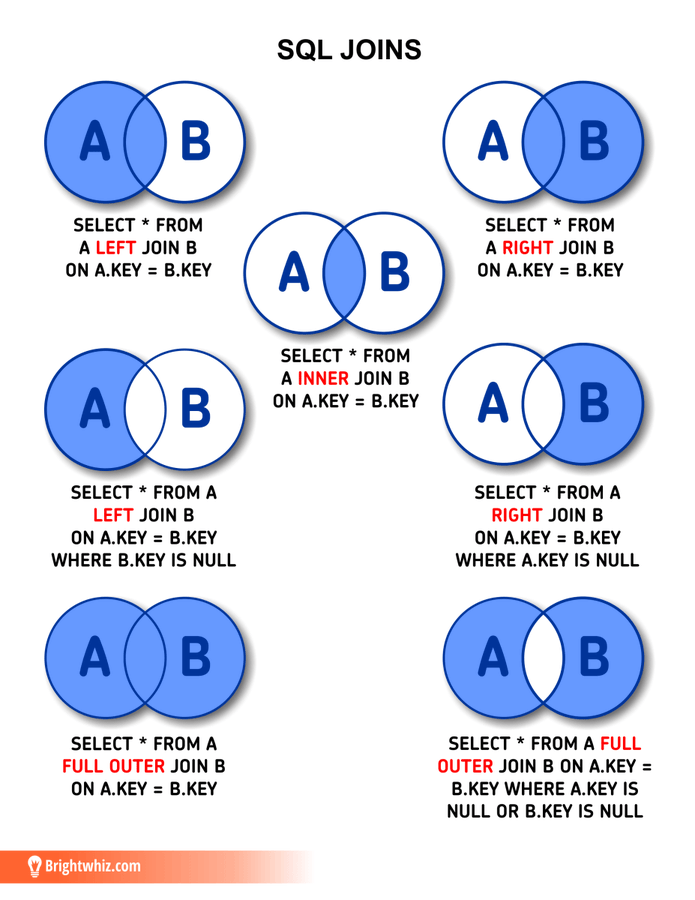
Inner join
SELECT *
FROM books
JOIN authors
ON books.author_id = authors.id;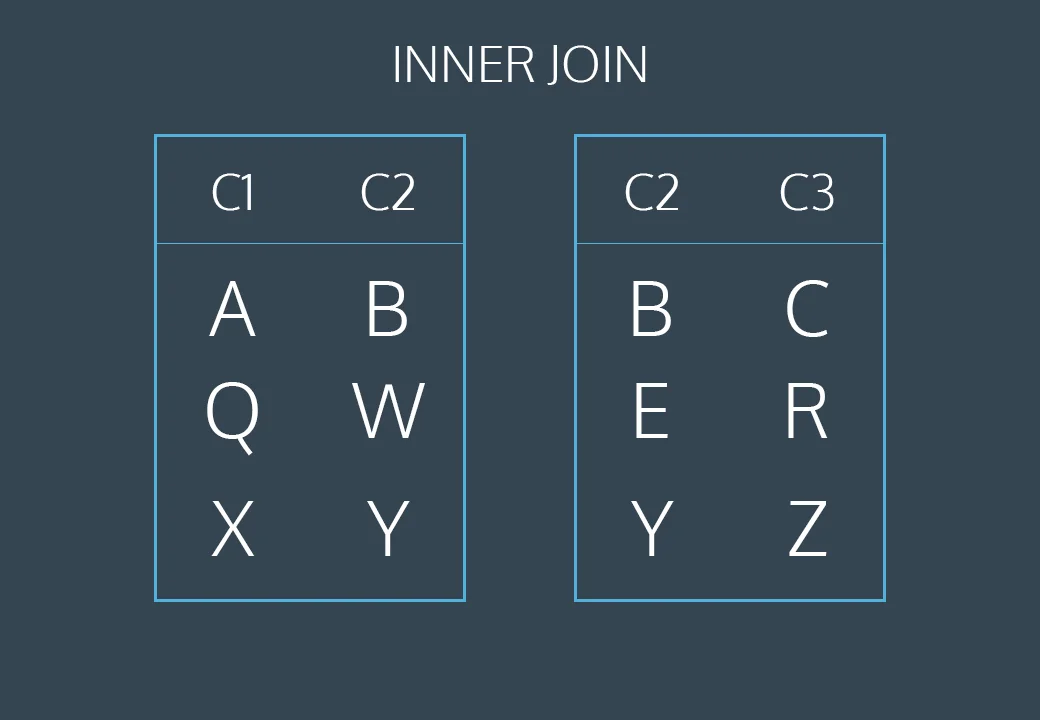
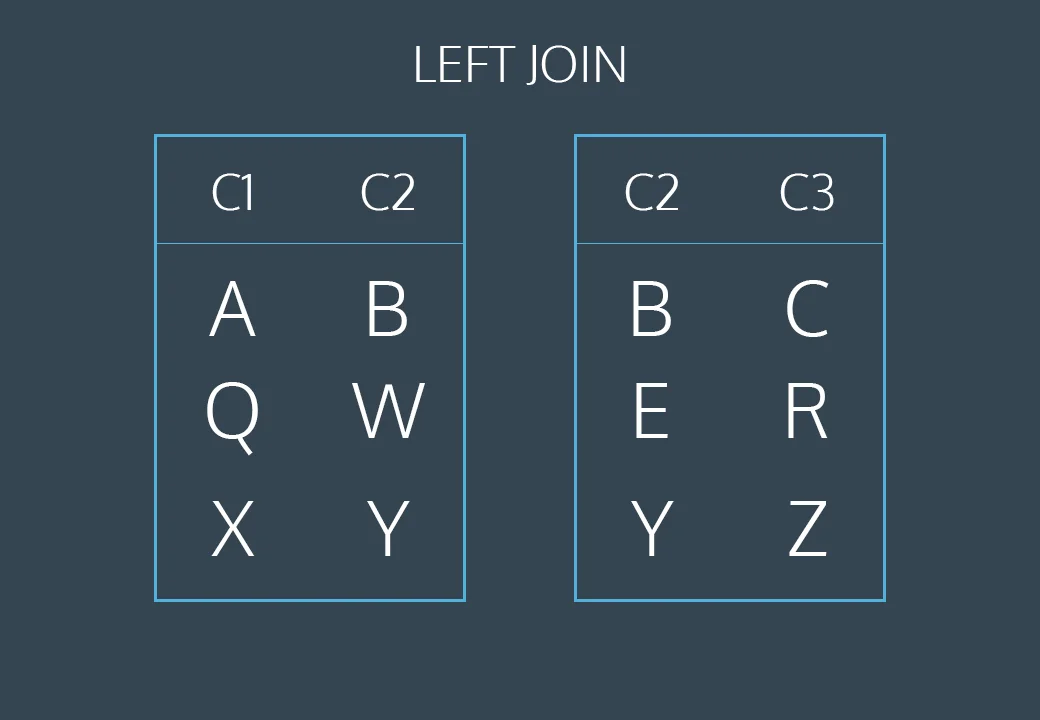
Left join
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;